Scheme of loss of milk teeth in children
All baby teeth erupt in children up to 2.5-3 years of age, after which, for some time, the issues of dentistry, as a rule, do not bother either kids or parents. However, the child gradually matures and it is time for new teeth - permanent. So they cut through, first fall dairy. It is important for parents to know when and how this happens in order to find their way in time for possible problems.
When the shift begins: key features
The beginning of the change of teeth individually for each child, but for most children this process is activated at 5-6 years of age. While the roots of the incisors begin to dissolve, the “sixes” grow in the children - the teeth that cut right after the second molars. These are the first permanent teeth appearing before the moment when the first baby tooth falls out. They are called the first molars, while milk molars are replaced with teeth after the loss, which are called “premolars”.
Signs that the child will soon have baby teeth and begin to cut permanent are:
- The appearance of gaps, as the child's jaw grows and the distance between the molars, canines and incisors expands.
- Reeling due to resorption of their roots.
- Begin teething permanent teeth. Sometimes they appear when the milk teeth are still unsteady, staying close by.
When do they start falling out?
The process of loss begins with the resorption of their roots. It is quite long - the roots of the incisors dissolve within two years, and the roots of the molars and canines can dissolve for three years or longer. As soon as the root resolves, the tooth will fall out and will give the chance to erupt into the permanent tooth.
In most babies, the first fallen tooth is found at the age of 6-7 years.
How much and when do they drop out?
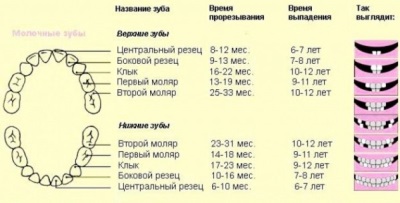
The scheme of loss of milk teeth is as follows:
- The first in most children fall central incisors on the lower jaw.
- After them comes the turn of the upper pair of central incisors.
- The next often fall lateral incisors on the upper jaw.
- Next comes the time of the fallout of the lower lateral incisors.
- After them, the first molars begin to fall out - first the upper pair, and then the pair on the lower jaw.
- When the molars fell out, the fang line comes. First, the upper pair (“eye” teeth) falls out, and then the canines on the lower jaw.
- Next come the second molars below.
- After them, the process of precipitation is completed by the upper second molars.
The approximate time of resorption of roots and loss of milk teeth is presented in the table:
|
When the roots dissolve |
When teeth fall out |
|
Central incisors |
|
|
From the age of 5 |
At the age of 6-8 years |
|
Side cutters |
|
|
From 5-6 years |
About 7-8 years old |
|
First molars |
|
|
From 6-7 years old |
Aged 8 to 11 years old |
|
Fangs |
|
|
From 7-8 years |
At 9-12 years old |
|
Second molars |
|
|
From 7-8 years |
Aged 10 to 13 years |
Do all baby teeth fall out?
All of them should fall out. There are twenty of them, among which there are 8 incisors, 4 canines and 8 molars. Some mothers think that chewing teeth (molars) in babies do not fall out, but this is not so. All of them fall out from the age of 6, since permanent ones will grow in their place.
How many times do you fall out?
In most cases, the teeth that erupt in a child in the first two years of life, fall out only once. All of them are replaced by permanent ones, but due to the expansion of the jaw between fangs and molars, two more teeth (premolar) appear. By the age of 17, most children have 28 permanent teeth, and the remaining 4 "wisdom teeth" erupt later (sometimes after 25-30 years).
Permanent teeth normally should not fall out, but there are cases when children erupt and fall out of several sets of teeth.
What factors influence the loss process?
If you violate the terms of loss immediately panic is not necessary, because this process depends on many factors. Doctors consider acceptable deviation from the average time for 1-2 years. The loss of milk teeth and the eruption of permanent affects:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Gender baby. It is noted that in boys the teeth fall out later.
- Problems during pregnancy.
- The duration of breastfeeding.
- Baby food intake.
- Chronic disease in the crumbs.
- The quality of drinking water consumed by the child.
- The climate in which the baby lives.
- Having a child with problems with the endocrine system.
- Infected childhood infections.
What if the tooth fell out?
When a child reports a dropped tooth, parents should:
- In case of bleeding from the hole, apply clean gauze to the wound and press with other teeth for several minutes. Treat the wound with antiseptic agents can not.
- Do not give the child food for two hours, and then do not feed the crumbs for a while very hot, salty or spicy foods. Also, do not give your baby solid foods, such as crackers or nuts. The best dishes in this case will be soups and porridges, and after eating your mouth should be rinsed with clean water.
- Warn the child that the hole formed does not need to be touched with his hands or tongue so that infection does not get into it.
- The tooth itself can be "given to the mouse", put under the pillow for the "fairies", exchanged for some gift or come up with something else. The main thing is that the child is not afraid and did not experience negative emotions.
Why fall out of time?
Before deadline
Too early loss is called when it falls out or is removed by a dentist before the age of 5. To lose a baby tooth ahead of time can be due to:
- Injuries due to a blow or fall.
- Tumor process in the mouth.
- Running caries when a tooth has to be removed.
- Malocclusion Incorrectly grown teeth can put pressure on one of them and provoke an earlier loss.
- Intentional loosening of his child.
The main problem of too early tooth loss is the displacement of the dentition, due to which permanent teeth can erupt crookedly. The child will have to adjust their position in the future.
Later than expected
The delay in the loss of milk teeth is possible due to:
- Malnutrition, due to which the child has a nutritional deficiency.
- Frequent stress.
- Chronic infections, such as tonsillitis.
- Rahita
- The effects of hereditary factors.
When to consult a doctor?
A child should be examined by a dentist if:
- From the wound after falling for a long time oozing blood.
- When the tooth fell out, the child's temperature rose, and the baby's condition worsened.
- The child was 6 years old, and the intervals between the milk teeth did not increase.
- The child did not fall out all the milk teeth by the age of 16-17 years.
- Milk or permanent teeth are affected by caries.
- The molar tooth was cut next to the milky one, while the milky one is not staggering or tottering, but did not fall out within three months after the appearance of the molar one.
After watching the next video, you can learn more useful information about how and at what age milk teeth change.
You will learn more by watching Dr. Komarovsky’s program.